Our teams provide complete handholding in preparation for a tax enquiry, investigation or appellate matter and work as business partners in dealing with regulatory authorities. Transfer pricing professionals provide effective guidance to your finance teams in maintaining country files and related.”
FinAccy as a tax consultant offers variety of services to its client few of them are:
1. Advisory & Planning Services
- Tax Preparation Service & Tax Return Filing
- Location Benefits
- Industry Benefits
- Selection of Tax incentive
- Double tax Treaty Benefits
- Withholding Taxes
- Transfer Pricing
2. Compliance Services
- Review of Tax Returns
- Payment of Taxes
- Prescribed Tax filings
- Tax Audit
3. Representation Services
- Before various Tax authorities
- Before Tax Appellate Authorities
- Before Tax Tribunals
Tax Preparation Services & Income Tax Return Filing
Income tax filing is the process of declaring of income and the resultant tax by the assessee in the prescribed form.
Following assessees are required to file return of income compulsorily:
- A company or firm
- A person other than a company or a firm to file income tax return if his or her income exceeds the basic exemption limit.
- A resident individual who has an asset located outside of India (might include financial interest in some entity as well) OR any resident who retains signing authority for an account based outside India shall mandatorily file return in the prescribed form.
(Note: Basic exemption limit refers to a term which means “maximum amount of income not chargeable to tax”. In simpler words, it means the highest amount of income on which tax shall not be payable)
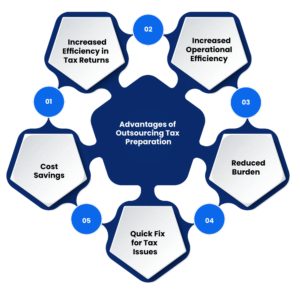
Advantage of Outsourcing Tax Preparation Service:
Due date of filing return of income:
| 31st October of the Assessment Year | 31st July of the Assessment Year |
| •a company; •a person (other than company) whose accounts are required to be audited; or •a partner of a firm whose accounts are required to be audited. | •For Other Assessee |
Heads of Income:
There are five heads under which income can be classified. These are:- Income From Salaries
- Income from House Property
- Profits & gains from Business or Profession
- Capital gains
- Income from other sources
| BENEFITS OF FILING WITHIN DUE DATE | DISADVANTAGES OF NOT FILING WITHIN DUE DATE |
| 1. Eligible to carry forward & set off the loss | 1. Not eligible to carry forward & set off the loss |
| 2. Pay lesser tax due to setting off loss against income | 2. Pay higher tax due to non-setting off loss against income |
Types of ITR forms:
| Who Can File | |
| ITR - 1 | This is also known as the Sahaj form. People who live in India and earn up to Rs 50 lakh annually are qualified for this. Anyone who receives income from a job, a single house property, or other sources such as horse races, lotteries, etc is eligible to submit an ITR1. However, NRIs are not eligible to submit ITR1. Those who were required to pay more than Rs. 25,000 in TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) in the prior year may also submit ITR 1 |
| ITR - 2 | Individuals and HUF who receive income from sources other than their business or line of work. The individual’s annual income must exceed Rs. 50 lakhs and income from agriculture must exceed Rs. 5000.ITR2 can be filed by individuals and NRIs who make money from a job, a home, capital gains, or other means. Those who receive their income from the sale of assets or properties are qualified to file ITR 2. Salaried people who have benefited from stock purchases and sales or suffered losses may submit an ITR-2 too. |
| ITR - 3 | Individuals and HUFs that derive their revenue from a profession or a sole proprietorship must select this form. A person must disclose any income they receive from a business or job. ITR3 must be filed by salaried individuals who make money through dealing in futures and options or intraday stock exchange. ITR3 can be used by individuals to track income from employment, real estate,capital gains, businesses, or trades (including presumed income), among other sources. |
| ITR - 4 | It is also known by the name Sugam. ITR 4 designates that this form may be used to submit IT returns by people who own a business and receive income from it as well as from other occupations. When a business has a turnover of up to Rs 2 crore and is liable to section 44AD taxation, its revenue is reported using the ITR-4 form. Additionally, ITR-4 is for income from a profession that is liable to section 44ADA taxation and has a turnover of up to Rs 50 lakh. Moreover, a freelancer who performs work in a notified occupation may submit an ITR-4. This form can also be used to submit an ITR for taxpayers who work as physicians, business owners, designers, retailers, agents, contractors, etc. Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) cannot choose this form, though. |
| ITR - 5 | The ITR-5 form must be opted for by Investment Funds, Business Trusts, Estate of the deceased and insolvent, Cooperative societies, Local authorities, Artificial Judicial Persons (AJPs), Bodies of Individuals (BOIs), Associations of Persons (AOPs), Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs), and firms. In order to disclose profits from their businesses and professions as well as some other sources of revenue, these alliance companies submit ITR-5s. |
| ITR - 6 | All companies may choose ITR 6, with the exception of those seeking Section 11 exemption. Housing property rental revenue, business income, and Multiple sources of income must be disclosed on ITR 6. Companies are only permitted to file returns online under this section. |
| ITR - 7 | A charitable or religious trust, a political group, a science research organization, a news agency, a hospital, a trade union, a university, a college, or other organizations such as an NGO or related organizations are all examples of people. |
| Form | Applicable to | Salaried | Exempt Income | Capital Gains | House Property | Business Income | Other Sources |
| ITR 1 | Resident Indian individuals and Hindu Undivided Families | Yes | Exempt however income from agriculture must not exceed Rs. 5000. | No Capital Gains | It can only be one house property. | No income from the business. | Yes |
| ITR 2 | Hindu Undivided Family and Individuals | Yes | Yes | No Capital Gains | Yes | No income from the business. | Yes |
| ITR 3 | Hindu Undivided Family, Individuals or Partner in a firm | Yes | Yes | No Capital Gains | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ITR 4 | Hindu Undivided Family, Individuals or Firm | Yes | Exempt however income from agriculture must not exceed Rs. 5000. | Yes | It can only be one house property. | Specifically for presumed business revenue only | Yes |
| ITR 5 | Limited Liability Partnerships or Partnership Firms | No | Yes | No Capital Gains | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ITR 6 | Companies | No | Yes | No Capital Gains | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ITR 7 | Trusts | No | Yes | No Capital Gains | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Income Tax Filing Due Dates for Financial Year
| Category Of Taxpayer | Due Date for Tax Filing *(unless extended) |
| Individual / HUF/ AOP/ BOI (books of accounts not required to be audited) | 31st July |
| Businesses (Requiring Audit) | 31st October |
| Businesses requiring transfer pricing reports (in case of international/specified domestic transactions) | 30th November |
| Revised return | 31 December |
| Belated/late return | 31 December |
| Updated return | 31 March(2 years from the end of the relevant Assessment Year) |
Consequences of Missing the ITR Filing Deadline
Interest
If you submit your return after the deadline, you will be liable to pay interest at a rate of 1% per month or part month on the unpaid tax amount as per Section 234A.
Late fee
In case of late filing, Section 234F imposes a late fee of Rs.5,000, which shall be reduced to Rs.1,000 if your total income is below Rs.5 lakh.
Loss Adjustment
In case you have incurred losses from sources like the stock market, mutual funds, properties, or any of your businesses, you have the option to carry them forward and offset them against your income in the subsequent year. This provision substantially reduces your tax liability in future years. However, you will not be allowed to carry forward these losses if you miss filing your ITR before the deadline.
Actions to Take If You Miss the ITR Filing Deadline
Belated Return
If you miss the ITR filing due date, you can file a return after the due date, called a belated return. However, you will still have to pay the late fee and interest charges, and you will not be allowed to carry forward any losses for future adjustments. The last date for filing a belated return is 31st December of the assessment year (unless extended by the government). Therefore, for this year, you may submit the belated return by 31 December at the latest.
Updated return
IStill, if you miss the 31st December deadline due to unavoidable reasons still you can file the updated (ITR U) return subject to the conditions specified therein.
Important Due Dates for Paying Advance Tax Instalments for Financial Year
Whenever we talk about income tax, there are certain tax formalities that need to be followed within the specified due dates, such as filing income tax returns, paying advance tax on time, etc.
The due dates for the payment of advance tax are:
| Due date | Nature of compliance | Tax to be paid |
| 15th June | First instalment | 15% of tax liability |
| 15th September | Second instalment | 45% of tax liability |
| 15th December | Third Instalment | 75% of tax liability |
| 15th March | Fourth instalment | 100% of tax liability |
| 15th March | Presumptive scheme | 100% of tax liability |
Clients Testimonials
Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I am very happyTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Very good experience with Finaccy business solutions LLPTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I had a good experienceTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Very good work experienceTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. This firm has been an exceptional partner in managing our business finances. Their team is knowledgeable, professional, and always up to date with the latest tax regulations. What I appreciate most is their personalized approach. Their attention to detail, responsiveness, and transparency in pricing have been invaluable. We now feel confident in our financial future, thanks to their expert guidance. Highly recommended for any accounting needs!Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Excellent experience with him. Right solution on right time.
